I reproduce some of the plots from Rstudio’s ggplot2 cheat sheet using Base R graphics. I didn’t try to pretty up these plots, but you should.
I use this dataset

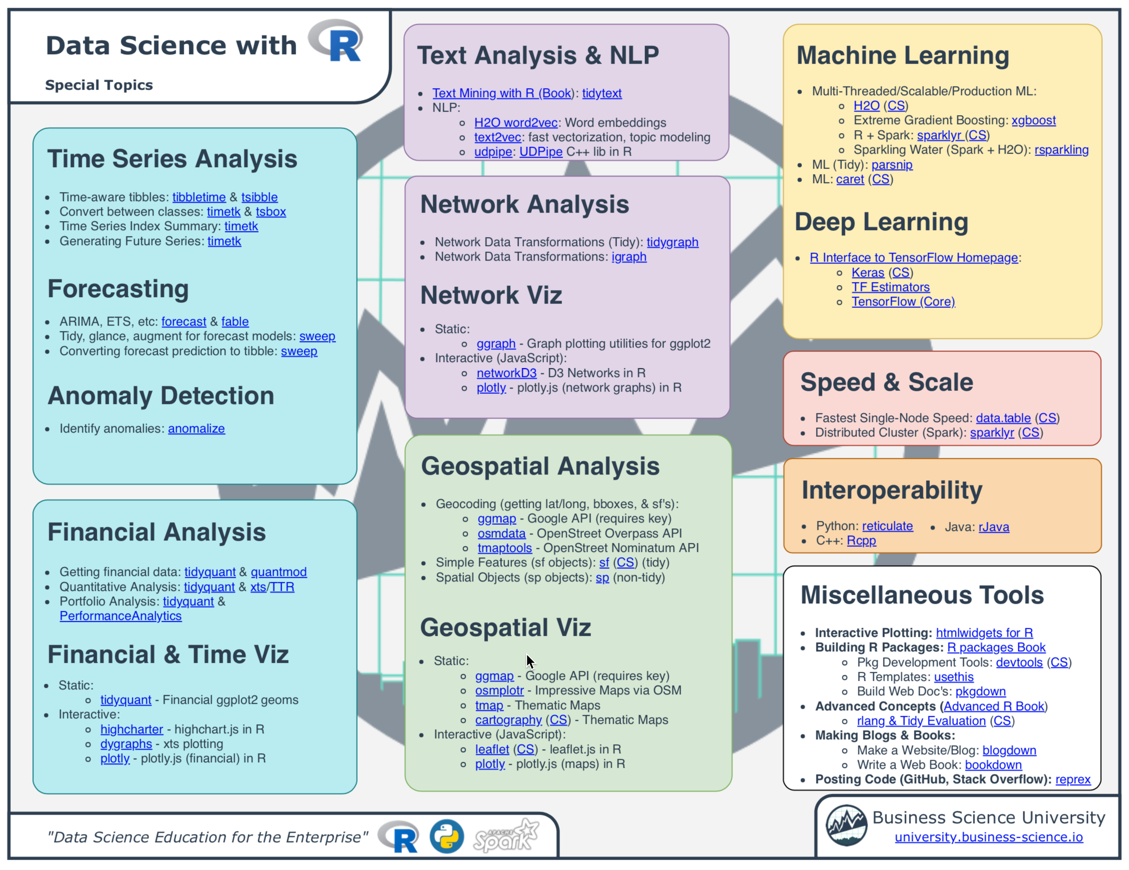
Base R Graphics Cheat Sheet David Gerard August 8, 2017. Abstract: I reproduce some of the plots from Rstudio’s ggplot2 cheat sheet using Base R graphics. Dplyr provides a grammar for manipulating tables in R. This cheat sheet will guide you through the grammar, reminding you how to select, filter, arrange, mutate, summarise, group, and join data frames and tibbles. Updated January 2017. R has 657 built in color names To see a list of names: colors These colors are displayed on P. R color cheatsheet Finding a good color scheme for presenting data can be challenging. This color cheatsheet will help! R uses hexadecimal to represent colors Hexadecimal is a base. R Syntax Comparison:: CHEAT SHEET Even within one syntax, there are o'en variations that are equally valid. As a case study, let’s look at the ggplot2 syntax. Ggplot2 is the plotting package that lives within the tidyverse. If you read down this column, all the code here produces the same graphic. Quickplot ggplot.
The main functions that I generally use for plotting are
- Plotting Functions
plot: Makes scatterplots, line plots, among other plots.lines: Adds lines to an already-made plot.par: Change plotting options.hist: Makes a histogram.boxplot: Makes a boxplot.text: Adds text to an already-made plot.legend: Adds a legend to an already-made plot.mosaicplot: Makes a mosaic plot.barplot: Makes a bar plot.jitter: Adds a small value to data (so points don’t overlap on a plot).rug: Adds a rugplot to an already-made plot.polygon: Adds a shape to an already-made plot.points: Adds a scatterplot to an already-made plot.mtext: Adds text on the edges of an already-made plot.
- Sometimes needed to transform data (or make new data) to make appropriate plots:
table: Builds frequency and two-way tables.density: Calculates the density.loess: Calculates a smooth line.predict: Predicts new values based on a model.
All of the plotting functions have arguments that control the way the plot looks. You should read about these arguments. In particular, read carefully the help page ?plot.default. Useful ones are:
main: This controls the title.xlab,ylab: These control the x and y axis labels.col: This will control the color of the lines/points/areas.cex: This will control the size of points.pch: The type of point (circle, dot, triangle, etc…)lwd: Line width.lty: Line type (solid, dashed, dotted, etc…).
Discrete
Barplot
Different type of bar plot
Continuous X, Continuous Y
Scatterplot
Jitter points to account for overlaying points.
Add a rug plot
Add a Loess Smoother
Cheat Sheet Roberts Rules Of Order
Loess smoother with upper and lower 95% confidence bands
Rdp with windows 10 home. Loess smoother with upper and lower 95% confidence bands and that fancy shading from ggplot2.
Add text to a plot
Discrete X, Discrete Y
Mosaic Plot
Cheat Sheet Re2
Color code a scatterplot by a categorical variable and add a legend.
Cheat Sheet Reviews
par sets the graphics options, where mfrow is the parameter controling the facets.
The first line sets the new options and saves the old options in the list old_options. The last line reinstates the old options.
Cheat Sheet Ruler
This R Markdown site was created with workflowr
